Nerve Net Describes the Nervous System of
This chapter describes the peptidergic nervous system of coelenterates the various types of neuropeptides and the biosynthesis of neuropeptides in coelenterates. A pair of closely united white pear-shaped cerebral or supra-pharyngeal ganglia forming the so-called brain.
Myelin insulates the nerve and helps the messages get through.

. The Cnidaria have a nerve net where the sensory and ganglionic neurons and their proc-esses are interspersed among the epithelial cells of both layers as an indication of a diffused nervous system. They only have one type of nerve cell that has short branches branch in multiple directions and are unmyelinated. Your brain and spinal cord make up your CNS.
Chemical secreted in response to an action potential which carries a chemical signal across a synapse from one neurone to the next generating a new action potential. 6Give 2 examples of neurotransmitters. This kind of expansive nerve net is also known as a diffuse nerve net.
The nervous system is a complex network of nerves and cells that carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord to various parts of the body. In orange you can see the nervous system. A neuron is a specialized cell involved in transmitting nerve impulses.
Nerves are found only in the peripheral nervous system. Communication between neurons can be in both directions at the synapse within a nerve net. The peripheral nervous system PNS and the central nervous system CNSThe CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord.
Comprises of cerebral ganglia or supra-pharyngeal ganglia circumpharyngeal connectives and subpharyngeal ganglia. Your peripheral nervous system consists. This unit describes methods for loading ion- and voltage-sensitive dyes into neurons with a particular focus on the spinal cord as a model system.
Although the protocols described here concern spinal networks in. A nerve is a whitish fiber of neuron cells which carry impulses to the central nervous system and from the central nervous system to the effector organs. Comparative studies of neurodevelopment in cnidarians and bilaterians suggest that this process began with distinct integration centres that evolved on opposite ends of an initial nerve net.
The nerve net is concentrated around the mouth. The human nervous system can be divided into two interacting subsystems. In bilaterian animals which make up the great majority of existing species the nervous system has a common structure that originated early in the Ediacaran period over 550 million years ago.
In addition to the nerve net several cnidarian species have appeared to have a considerable degree of regionalization of the neural structure. The nervous system within the flatworms are organized within a very different way from the other invertebrates. The study of the evolutionary development of the nervous system traditionally concentrated on the structural differences that exist at various levels of the phylogenetic scale but certain functional characteristics including biochemical and biophysical processes laid down early in evolution and amazingly well conserved to the present can no longer be ignored.
Cephalized animals have brains of varying complexity. In addition we describe the use of these dyes to visualize neural activity. The puzzle of how complex nervous systems emerged remains unsolved.
The hydra has a nervous system characterized by a nerve net. Complex brains are typically compartmentalized with separate but interconnected structures for functions such as olfaction vision and integration. View the full answer.
Central nervous system CNS. The Cnidaria have a nerve net where the sensory and ganglionic neurons and their processes are interspersed among the epithelial cells of both layers as an indication of a diffused nervous system. The main parts of the nervous system are.
In addition to the nerve net several cnidarian species have appeared to have a considerable degree of regionalization of the neural structure. The nervous system of the worm is composed of bilobed cerebral ganglion connected to the circumpharyngeal connectives followed by the sub-esophageal ganglion and the nerve cord extended throughout. In radially symmetric animals such as the jellyfish and hydra the nervous system consists of a nerve net a diffuse network of isolated cells.
Describe the general features of a nerve net They are found in simple organisms like the hydra and are a type of nervous system that lacks a co-ordinatorbrain. They generally does not have any nerve net but they are connected with the help of long nerve cords. Neurons are connected by synapse.
The presence of chemical synapses in the coelenterate nervous system is confirmed by simultaneous intracellular recordings at both pre- and postsynaptic neurones which display the. The nerve cords are connected to the. Your brain uses your nerves to send messages to the rest of your body.
In cnidarians the neurons are joined to epithelial receptors and to contractile cells. 1Synapses separate neurones sending the nervous impulse between them in 1 direction only. The peripheral nervous system is an extensive network of nerves connecting the CNS to the muscles and sensory structures.
Each nerve has a protective outer layer called myelin. This nerve net looks similar to an actual net but it is the brain of the animal. A nerve net is a collection of separate but connected neurons.
A diffuse nerve net is different from the radial or circular nerve net that is found in other radially symmetric animals. Ganglia located near the head with attached main nerves running. The apical nervous system controlled ge.
Nerve net primitive nerve arrangement forming the entire nervous system of many cnidarians and a part of more advanced nervous systems. It comprises of the anterior nerve ring or brain ring and the posterior ventral nerve cord. The diffuse nervous system of cnidarians can best be described as a nerve net.
A nerve net is a simple decentralized multipolar multipolar nervous system found in animals like jellyfish. Neurons are found in both peripheral and central. Sensory structures of cnidarians are distributed throughout the body and include receptors for perceiving touch and certain chemicals.
Cnidarian nerve cells interconnect to form a two dimensional nerve net. Cytoplasmic processes join the nerve cells neurons of nerve nets.

Anatomy Midterm Lecture Flashcards Quizlet

Basic Structure And Function Of The Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology I

Basic Structure And Function Of The Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology I

Project Muse Monsters On The Brain An Evolutionary Epistemology Of Horror Science Resources Social Science Johns Hopkins University

The Chart Shows Four Levels Organisms Which Statement Correctly Describes A Level Of Organization In Brainly Com

Which Measure Of Central Tendency Best Describes The Weight Of The Candy In 2022 Central Tendency Histogram Weight

Vestibulocochlear Nerve Pharmacology Nursing Anatomy Lessons Medical Dictionary
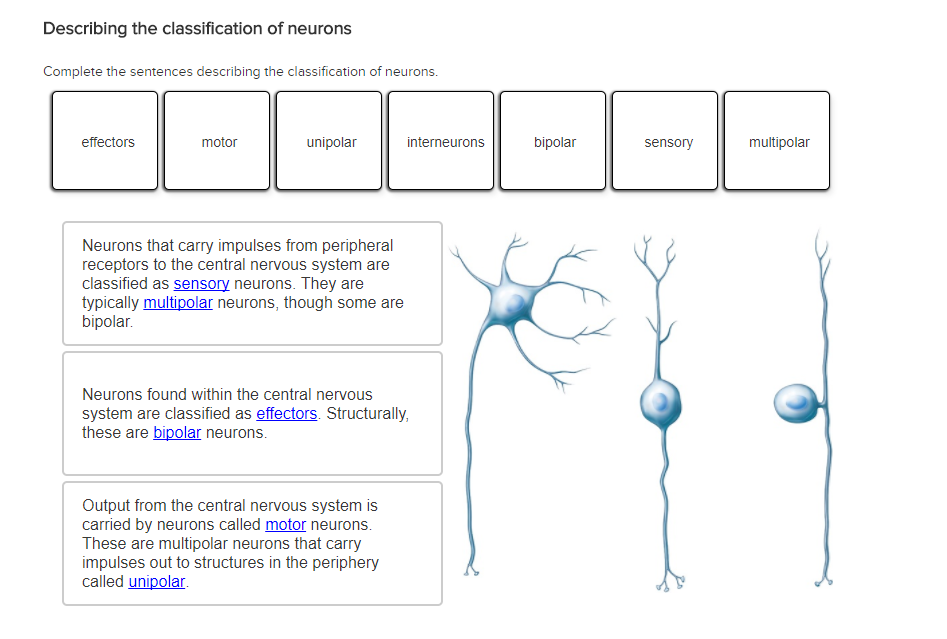
Solved Describing The Classification Of Neurons Complete Chegg Com

Nervous System 1 Introduction To The Nervous System Nursing Times

Basic Structure And Function Of The Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology I

Unit 9 The Nervous System Douglas College Human Anatomy Physiology I 2nd Ed

Basic Structure And Function Of The Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology I

Nervous System 1 Introduction To The Nervous System Nursing Times

This Picture Describes How Grey And White Matter Has A Vital Impact On Every Stage Of Physical And Mental Development Brain Facts Brain Structure White Matter



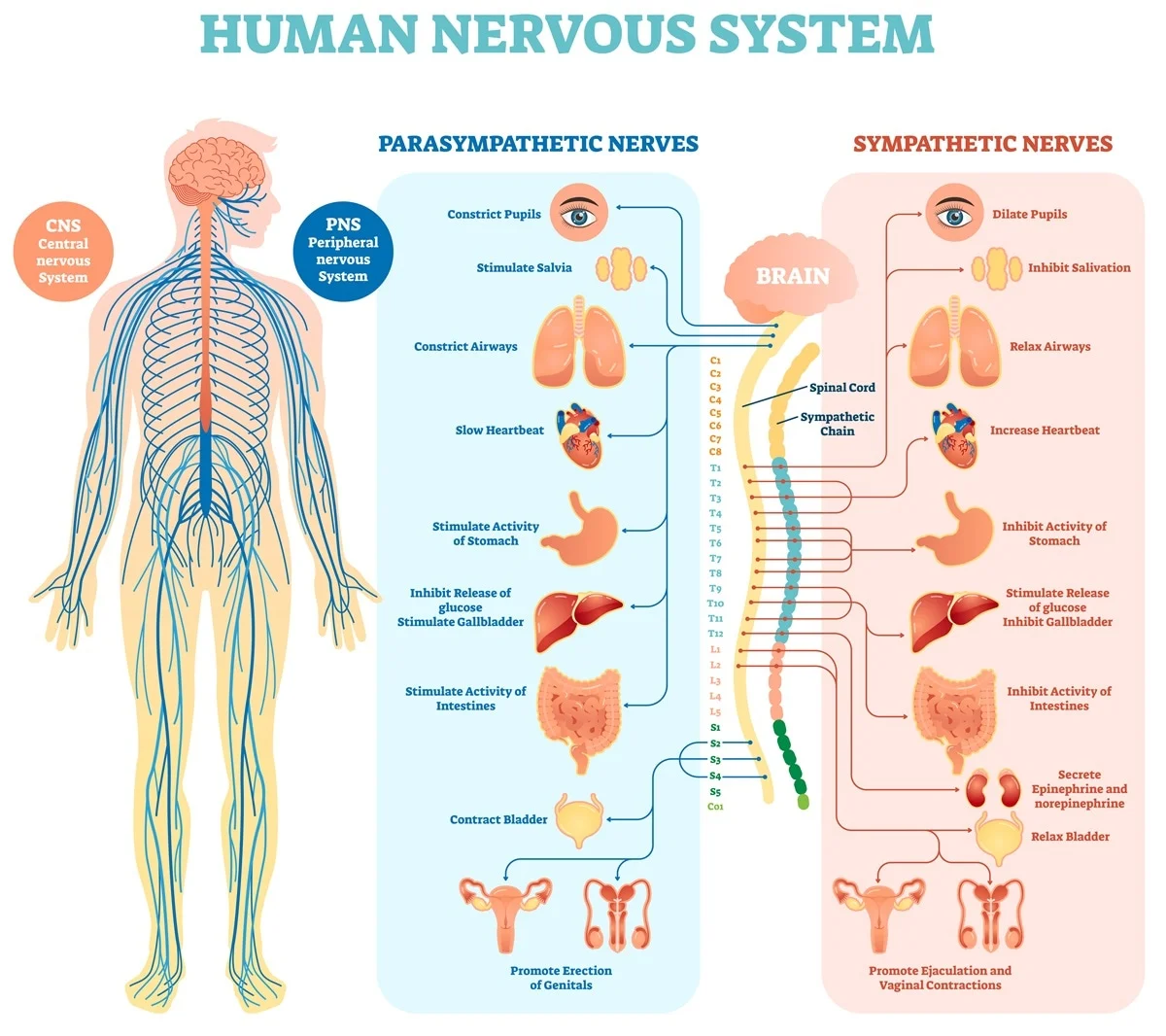


Comments
Post a Comment